If you’re an avid reader of my blog, you might remember my in-depth post on optimizing web browser performance. Today, I’m excited to share a game-changing tip that can potentially transform your browsing experience altogether: the art of tweaking Chrome’s hardware acceleration settings. If you’ve ever encountered frustrating visual glitches or sluggish behavior while using Chrome, this guide could be your savior.
In this article, we will explore the concept of hardware acceleration, its significance, and how you can customize it to fit your needs. So, let’s dive deep into this little-known feature and discover the wonders it can do for your browsing experience.
What is hardware acceleration?
At its core, hardware acceleration is a feature that allows certain software applications, including Google Chrome, to use the computer’s hardware directly, specifically the GPU (Graphics Processing Unit), to process and render visuals faster than it would by relying solely on the CPU.
Picture this: Imagine you are a painter and you’re trying to paint a large canvas. Without assistance, the process could be laborious and time-consuming. But if someone handed you a much larger brush (that’s our GPU in this analogy), you’d be able to cover more ground quickly and efficiently. That’s essentially what hardware acceleration does.
Why should I care about hardware acceleration?
The simple answer is performance. With hardware acceleration turned on:
- Web pages load faster: This is particularly true for sites heavy on visuals or animations.
- Videos play more smoothly: If you love binge-watching videos, this is a game-changer. Remember the last time your video playback was choppy? Hardware acceleration might have been the solution you were looking for.
- Less strain on your CPU: It redistributes tasks to the GPU, ensuring your computer runs more efficiently.
However, it’s not all sunshine and rainbows. At times, hardware acceleration can cause issues:
- Compatibility problems: Not all graphics cards play nicely with hardware acceleration, leading to visual glitches.
- Overheating issues: Your GPU might run hotter, which, in the long run, could cause wear and tear.
How to enable or disable hardware acceleration in Chrome
Here is your step-by-step guide to turn this feature on or off.
1. Open Google Chrome
Start with the basics. If you haven’t already, launch Google Chrome. I must say, every time I open Chrome, I marvel at its sleek design. Google has indeed done an incredible job with its aesthetics.
2. Access settings
On the top right corner of the Chrome window, you’ll see three vertical dots. Click on that. From the dropdown menu, scroll down and select “Settings”. I’ve often wished that Chrome had a more direct link to its settings on its homepage, but I guess a few extra clicks won’t hurt.
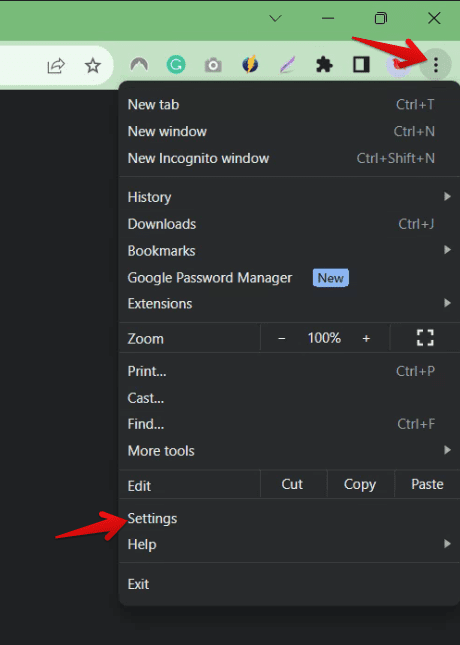
Launching Chrome Settings
3. Dive into advanced settings
Within the settings page, scroll all the way down until you see “Advanced”. Click on it. You will see additional settings unfold beneath.
4. Find the “System” section
Under the expanded advanced settings, locate the “System” section. Every time I enter this section, it feels like stepping into the cockpit of a spaceship. So many controls and so much power at my fingertips!
5. Toggle hardware acceleration
Here’s where the magic happens. In the “System” section, you will find an option that says “Use hardware acceleration when available”. There’s a switch right next to it. If the switch is blue, it’s turned on. If it’s grey, it’s turned off.
To enable hardware acceleration, click on the grey switch. It should turn blue. To disable hardware acceleration, click on the blue switch. It should turn grey.
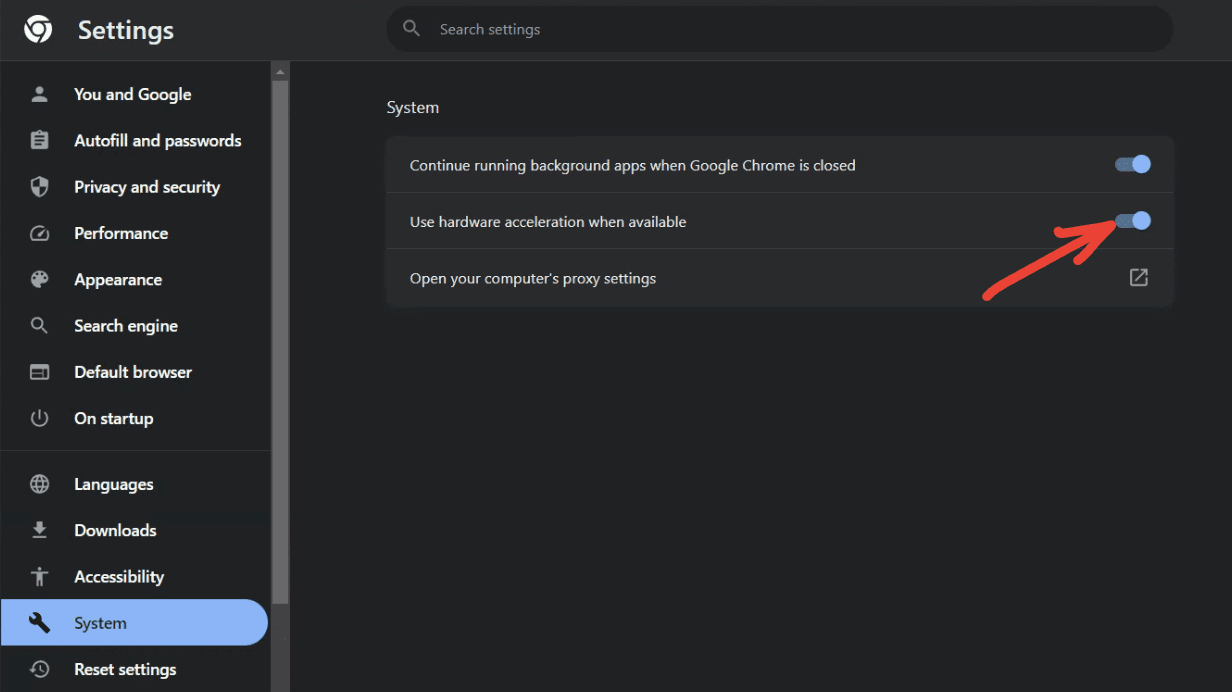
Enabling hardware acceleration on Chrome
6. Relaunch Chrome
For the changes to take effect, Chrome needs a fresh start. A button saying “Relaunch” should appear right after you toggle the hardware acceleration option. Click on it, and Chrome will restart.
To toggle or not to toggle?
Now, the question arises: should you have hardware acceleration turned on or off?
Enabling hardware acceleration in Chrome can significantly enhance your browsing experience. However, if you notice any unusual behavior, such as screen flickering or black boxes, it may be worth disabling it. Disabling hardware acceleration can be especially helpful when you’re troubleshooting issues with your browser. I vividly remember a time when I was working on a presentation for a workshop, and a specific website wouldn’t render correctly. It was only after I disabled hardware acceleration that everything worked as expected.
That being said, there may be times when disabling hardware acceleration is not necessary. For instance, when browsing graphic-heavy sites or streaming videos, it may be beneficial to have it enabled. Ultimately, the decision to enable or disable hardware acceleration should be based on your specific needs and preferences.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about hardware acceleration in Chrome:
In my time exploring and discussing hardware acceleration, I’ve come across a few recurring questions. I thought it’d be helpful to collate them here for anyone seeking quick answers:
1. Does hardware acceleration make Chrome faster?
Answer: Generally, yes. Hardware acceleration allows Chrome to offload some graphic-intensive tasks to the GPU, which can process these tasks faster than the CPU. This typically results in smoother animations, faster web page rendering, and improved video playback. However, the actual performance can vary based on your computer’s specifications.
2. Can hardware acceleration damage my computer?
Answer: No, hardware acceleration itself won’t damage your computer. However, it can make your GPU work harder, which might lead to increased temperatures. It’s always good practice to ensure your computer has adequate cooling and ventilation. If you notice your computer getting too hot, consider turning off hardware acceleration or checking for other underlying issues.
3. Why am I seeing visual glitches with hardware acceleration turned on?
Answer: This is likely due to compatibility issues between Chrome’s hardware acceleration and your GPU or its drivers. Turning off hardware acceleration often resolves these visual glitches. Additionally, ensuring your graphics drivers are up-to-date can help.
4. Will turning off hardware acceleration prolong my battery life?
Answer: It might. Using the GPU can consume more power, which may lead to faster battery drain. If you’re looking to conserve battery, especially on a laptop, you can try turning off hardware acceleration and see if it makes a difference.
5. Do other browsers have hardware acceleration too?
Answer: Yes, many modern web browsers, like Firefox and Microsoft Edge, also feature hardware acceleration. The steps to toggle it might differ, but the principle remains the same.
6. I turned off hardware acceleration, but Chrome still seems slow. What should I do?
Answer: Multiple factors can affect Chrome’s performance. It could be due to extensions you’ve installed, cached data, or even other software on your computer. Consider clearing Chrome’s cache, disabling unnecessary extensions, or checking for software conflicts.
7. Is there a shortcut to directly access hardware acceleration settings in Chrome?
Answer: While there’s no direct shortcut, you can type chrome://settings/system in the address bar to quickly jump to the system settings where the hardware acceleration toggle is located.
Final thoughts
Google Chrome’s hardware acceleration is a powerful tool that can enhance your browsing experience by using your computer’s graphics card to render web pages more quickly. However, it can also cause certain issues if not configured properly. It’s like a secret sauce that works behind the scenes, making your browsing experience smoother and faster.
As a user, it’s important to be aware of the different tools and options available to you. I encourage you to experiment and find out what works best for you, whether you’re an occasional browser or a power user. I hope this guide has been helpful in shedding light on this feature. So, happy browsing and keep exploring! Remember to stay curious and keep learning.
