For a long time, internet privacy and security have been major concerns for users worldwide. With the ever-increasing number of cyber threats, ensuring that your online activities are safe and secure has become imperative. Unsurprisingly, the most popular web browser, Google Chrome, offers several privacy and security features that can help protect your online identity and keep your browsing data private.
This comprehensive guide will dive deep into Chrome’s privacy and security settings and explain how you can configure them to enhance your online privacy.
Enhancing Chrome browser privacy & security
This guide is designed to help you make the most of Chrome’s features, whether you are a casual user or are deeply concerned with digital security issues. Are you looking to explore Google Chrome to the fullest? Here are 10 hidden Chrome browser features you probably didn’t know about.
Understanding Chrome’s privacy & security settings
Chrome’s privacy and security settings are designed to help users protect their online identity and keep their browsing data private. Understanding these settings is crucial to ensuring that you are in control of your online security.
Google Chrome privacy settings
The privacy settings allow users to control how their personal information is collected and used while browsing the internet. This includes blocking third-party cookies, disabling location tracking, and controlling what information is shared with websites. By enabling these, websites can be prevented from tracking your online activities and collecting personal information without your consent.
The security settings, however, are designed to protect users from online threats such as malware, phishing, and other attacks. These settings include enabling safe browsing, blocking malicious downloads, and sandboxing. With these, users can prevent unauthorized access to personal information and protect their devices from malware.
It’s important to note that while these settings can help enhance your privacy and security, they are not foolproof. Users should still exercise caution when browsing the internet and use common sense to avoid falling victim to scams and other security threats. The following sections will explore how to configure Chrome’s privacy and security settings.
Configuring Chrome’s privacy settings
Configuring Chrome’s privacy settings can help enhance your online privacy by preventing websites from tracking your online activities and collecting personal information.
Firstly, you must enable the Do Not Track option for all sites as default. This setting sends a signal to websites for not tracking your online activities. To enable this, go to Chrome’s settings, click on “Privacy and Security,” and toggle on the “Send a ‘Do Not Track’ request with your browsing traffic” option.
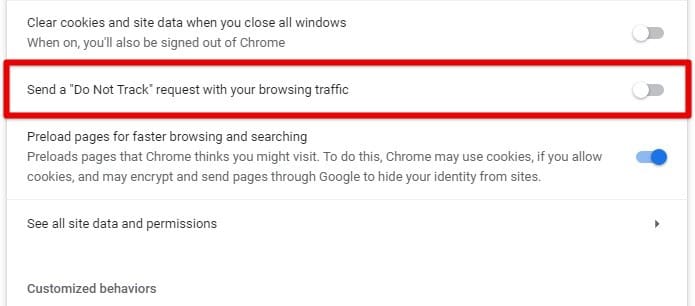
Do Not Track request
It is also essential to block third-party cookies. Advertisers and other websites use these to track your online activities across different sites. To block them, go to Chrome’s settings, click on “Privacy and Security,” then “Cookies and other site data,” and toggle the switch next to “Block third-party cookies”.
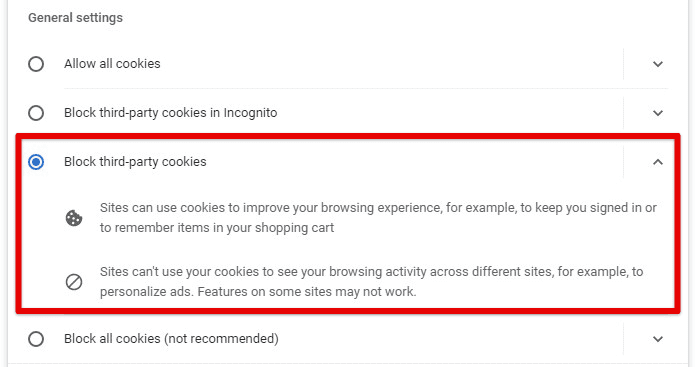
Blocking third-party cookies
Every Chrome user should also know how to manage their browsing history. Your browsing history can reveal a lot about your online activities. To manage it, go to Chrome’s settings, click “Privacy and Security,” then “Clear browsing data,” and select the data you want to clear, such as history, cookies, and cache.
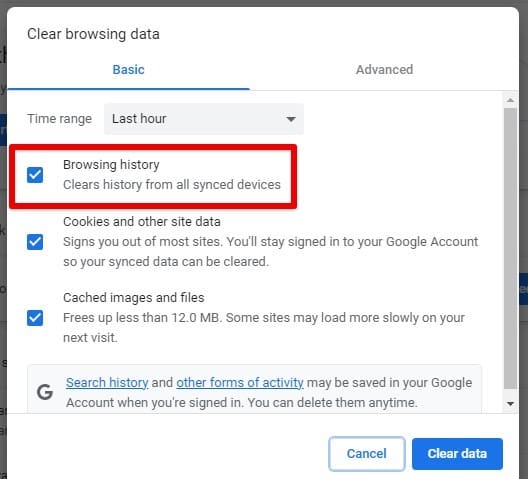
Clearing browsing history
The same is valid with managing site permissions: Websites may request access to your location, camera, microphone, and other personal information. To handle these, go to Chrome’s settings, click “Privacy and Security,” then “Site settings,” and select the permissions you want to manage.

Managing site permissions
Use a private browsing window for overly private and sensitive tasks. Chrome’s incognito mode allows you to browse the web without leaving traces of browsing history, cookies, or other online data. To use it, click the three-dot menu icon in the top-right corner and select “New incognito window.”

Private browsing with incognito mode
It’s important to remember that these settings may impact the functionality of certain websites or services, so you should always use your best judgment when deciding which settings to enable or disable.
Configuring Chrome’s security settings
Configuring Chrome’s security settings is essential to protect yourself against increasing online threats, scams, and attacks. Safe browsing warns you about potentially dangerous websites and downloads. Go to Chrome’s settings, click on “Privacy and Security,” then “Security,” and toggle on the “Safe browsing” option.
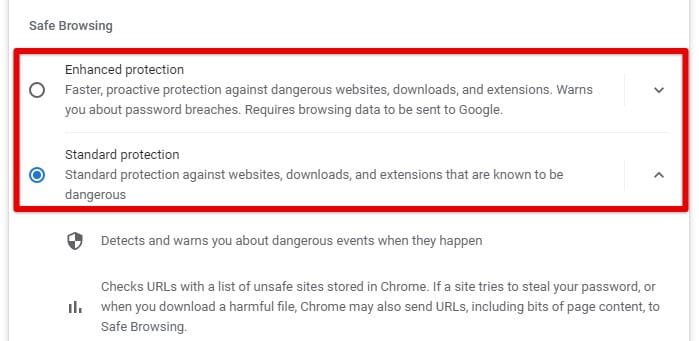
Safe browsing protection
Hackers can use pop-ups to trick you into downloading malware or visiting dangerous websites. To manage pop-ups, go to Chrome’s settings, click on “Privacy and Security,” then “Site settings,” and select “Pop-ups and redirects” to manage which sites are allowed to show pop-ups.
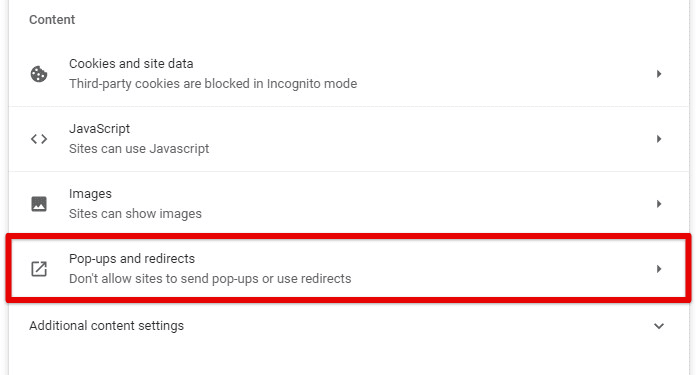
Managing pop-ups and redirects
Chrome’s sandboxing feature isolates websites and extensions from the rest of your device, reducing the risk of malware infections. To turn on sandboxing, go to “Privacy and Security” and toggle on the “Use sandbox” option.
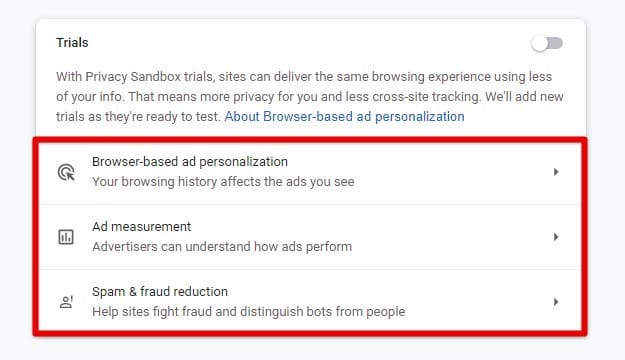
Privacy sandbox
Automatic downloads can install malware without your knowledge. To disable them, go to the “Privacy and Security” section and “Automatic downloads” to manage which sites can download files automatically in the background.
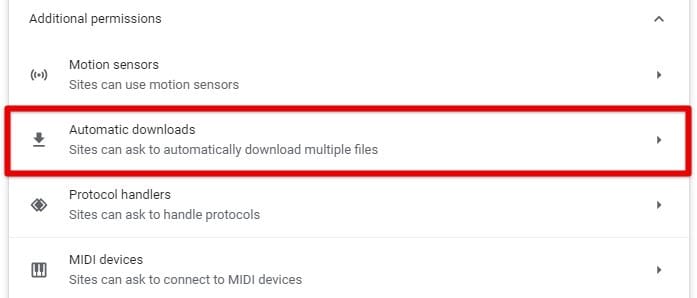
Managing automatic downloads
Browser extensions such as ad-blockers and anti-malware software can help protect you against online threats. To install these, go to Chrome’s Web Store and search for privacy and security extensions that other users have highly rated. Remember that no security setting is foolproof, so you should always use caution when browsing the internet and be mindful of potential security threats.
Incognito mode
Chrome’s incognito mode is a useful feature that allows you to browse the web without leaving any browsing traces, cookies, or other online data. Open a new Incognito window by clicking on the three-dot menu icon in the top right corner of Chrome and selecting “New incognito window”. Alternatively, you can use the keyboard shortcut Ctrl + Shift + N (Windows, Linux) or Command + Shift + N (Mac).
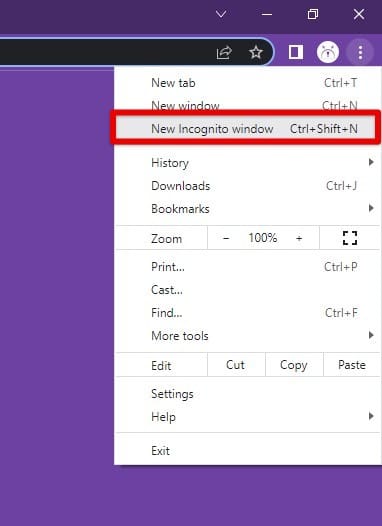
Opening a new incognito window
Once in incognito mode, you can browse the web just like in a regular Chrome session. Any websites you visit, cookies you download, or searches you make won’t be saved. When you’re done browsing, close the window. Any data you downloaded or viewed during that session will be erased immediately.
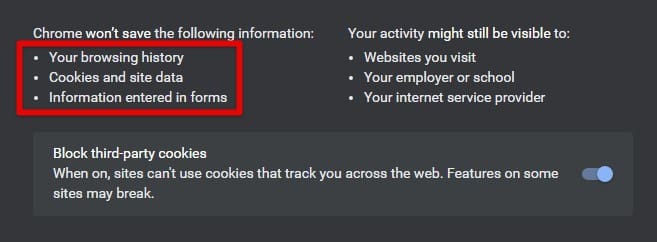
Information erasure in incognito mode
Note: While Incognito mode can help protect your privacy, it does not make you completely anonymous. Websites can still track your IP address and other information, and your internet service provider may also be able to see your online activities.
Additionally, any bookmarks you save, files you download, or passwords you enter while in incognito mode will still be saved to your Chrome browser unless you manually delete them. To ensure complete privacy, consider using a virtual private network (VPN) or other tools in addition to this mode.
Managing cookies
Cookies are small text files stored on the computer by websites you visit. They can be used to remember your preferences, login information, and browsing history. However, cookies can also be used to track online activities and potentially be a security risk.
To enable or disable cookies in Chrome, go to Chrome’s settings, click on the “Privacy and Security” tab, then select “Cookies and other site data.” You can set or deselect the “Allow all cookies” option from there.
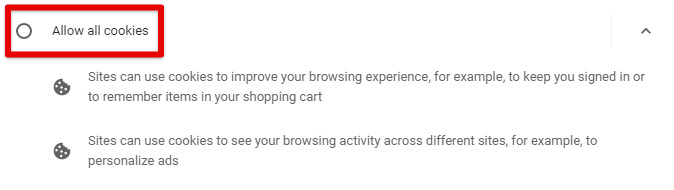
Enabling or disabling cookies on Chrome
For deleting individual cookies, go to the same page and search for a specific website. Click the “Remove” button next to the cookies you want to delete.
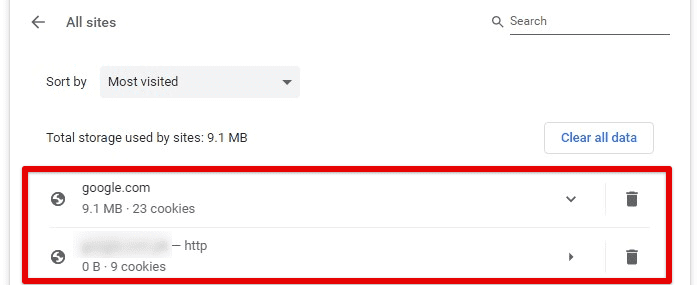
Removing cookies from a specific site
To delete all cookies, go to Chrome’s settings, click “Privacy and Security,” and then “Clear browsing data.” Next, select “Cookies and other site data” and choose the time range for which you want to delete these cookies. It is recommended to choose “All time”. Then click on the “Clear data” button to finish the process.
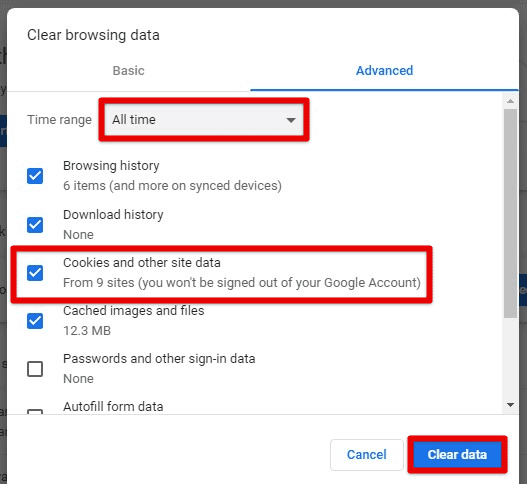
Clearing all cookies
To configure how cookies are handled in your browser, go to the “Privacy and Security” tab and select “Cookies and other site data”. From this page, choose whether to allow all cookies, block third-party cookies, or block all cookies.
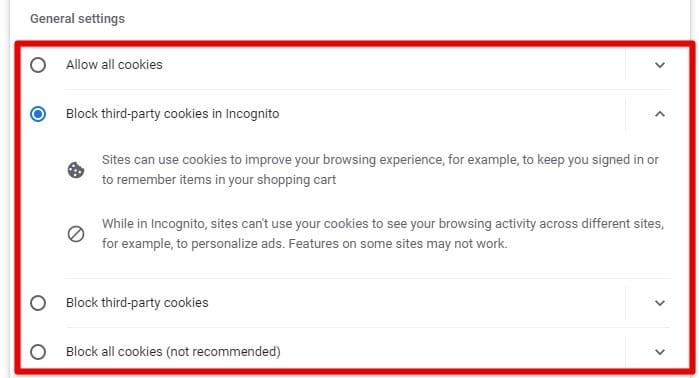
General settings for cookies
Do not forget that some websites may not function properly if you block all cookies, and some may be necessary for specific features or services to work. Do you have to use the same set of cookies in some other browser or device? Learn how to copy Google Chrome cookies to another computer.
Password management
Managing passwords is an important aspect of online security, and Chrome’s password management features can make it easy to create and store strong passwords. When you create a new account or change a password on a website, Chrome will offer to generate a solid and unique password for you. You can accept the password suggestion, and Chrome will automatically save it in the password manager.
Using Chrome on multiple devices, you can sync the saved passwords across all devices. To do this, sign in to Chrome with your Google account and turn on sync for passwords.
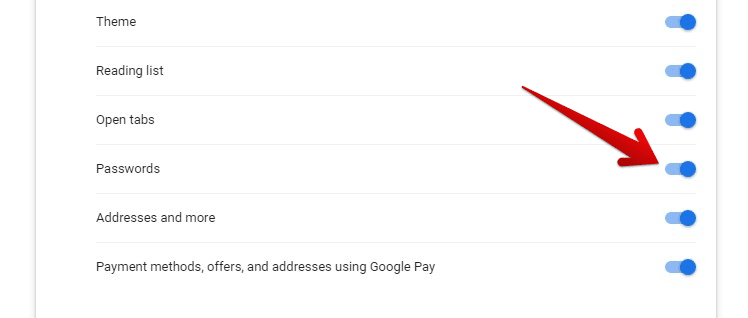
Turning on sync for passwords
You can access your saved passwords in Chrome’s password manager. To do this, go to Chrome’s settings, click “Passwords,” enter your computer password, or use biometric authentication. From there, viewing, editing, and deleting any saved password is possible.
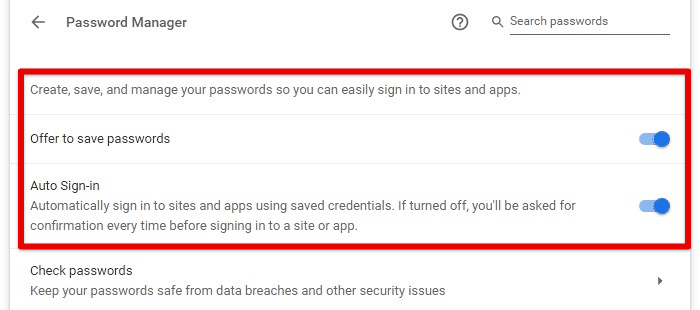
Google Chrome password manager
To add an extra layer of security to this catalog, enable two-factor authentication in Chrome. This requires you to enter a code from the phone or some other device in addition to your password when editing or viewing some entries in the manager.
With Chrome’s password management features, you can create and store strong, unique passwords for all online accounts, improving overall online security. Remember never to reuse passwords across multiple websites and to update them regularly.
Securing Chrome sync
Chrome Sync syncs your bookmarks, browsing history, saved passwords, and other data across multiple devices. Therefore, securing your Chrome Sync data is crucial to prevent unauthorized access.
Google Chrome sync
When you sign in to Chrome, use a strong and unique password that is difficult to guess. Avoid using the same password for multiple accounts, and use a combination of upper- and lower-case letters, numbers, and special characters.
Chrome Sync also allows you to enable two-factor authentication, which adds an extra layer of security to the account. When you sign in, you’ll be prompted to enter a code sent to your phone or another device besides the main password.
Google Chrome 2-step verification
You can also choose which data and settings will be synced from your Google account. If you don’t need something updated, like your browsing history, disable it from the settings. Also, it is important to sign out of Chrome when you’re not using it, especially if you are on a public computer or sharing a device with others.
Conclusion
Chrome’s privacy and security settings can help protect your online privacy and secure personal data. Understanding and configuring these settings allows one to customize Chrome to meet specific needs and preferences while minimizing online security threats. You can further enhance these safekeeping practices with features like an incognito mode and password manager. Moreover, remember to regularly review and update these to ensure you take advantage of the latest features.
Chrome web security can be pretty valuable to the end-user as it protects you from hackers or other applications that might aim to compromise the system’s security. Unfortunately, it can get annoying, especially for web development or penetration testing. Here is how you can disable Chrome Web Security flags on Chromebook.
